Food Datasets: Unlocking Data-Driven Intelligence Across the Global Food Ecosystem

The global food ecosystem has become one of the most data-intensive industries in the digital economy. From grocery delivery apps and food delivery platforms to restaurants, cloud kitchens, FMCG brands, and retailers, every interaction generates valuable data. This growing volume of structured and unstructured information is collectively referred to as food datasets.
Food datasets power decision-making across pricing, demand forecasting, menu optimization, supply chain management, nutrition analytics, and AI-driven personalization. As food consumption shifts increasingly toward digital platforms, access to accurate, real-time, and scalable food datasets has become a strategic advantage.
This blog explores what food datasets are, the types of data they include, how they are collected, key use cases across industries, challenges in food data collection, and why web scraping plays a critical role in building reliable food intelligence.
What Are Food Datasets?
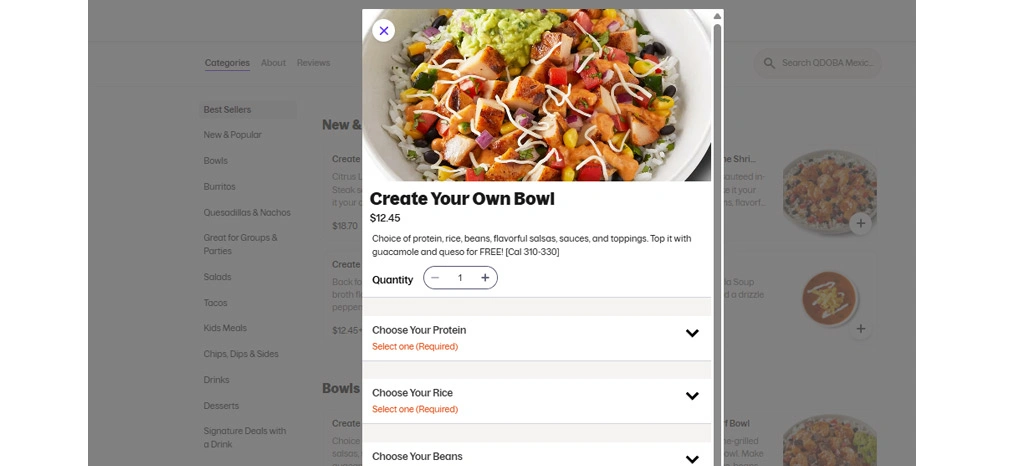
Food datasets are structured collections of data related to food products, menus, pricing, availability, nutrition, delivery performance, and consumer behavior. These datasets can originate from multiple digital touchpoints, including:
- Online grocery platforms
- Food delivery apps
- Restaurant websites and menus
- Quick commerce platforms
- Retail e-commerce stores
- Nutrition and ingredient databases
When organized properly, food datasets enable large-scale analysis, automation, and predictive insights across the food value chain.
Key Sources of Food Datasets
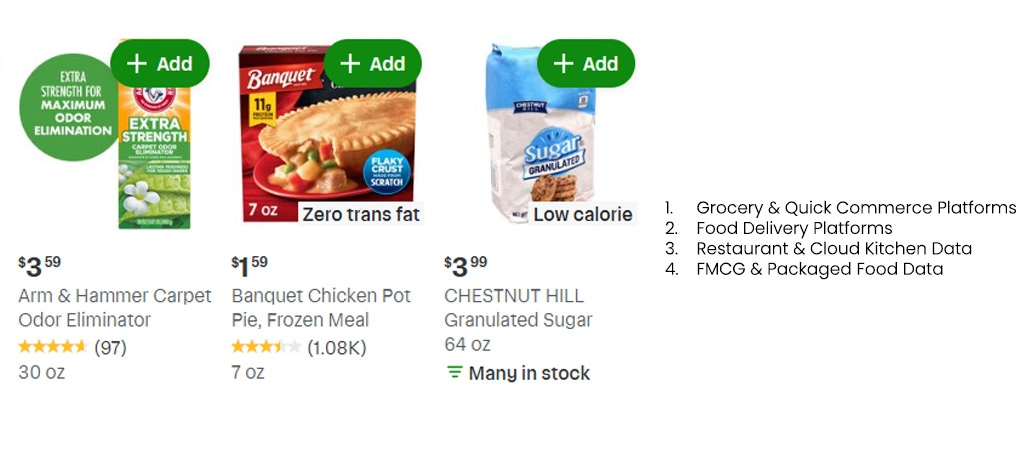
1. Grocery & Quick Commerce Platforms
Online grocery and quick commerce platforms generate rich datasets related to:
- Product catalogs
- Real-time pricing
- Discounts and promotions
- Stock availability
- Delivery timelines
These datasets are essential for retail price intelligence and assortment analysis.
2. Food Delivery Platforms
Food delivery apps provide datasets covering:
- Restaurant listings
- Menus and item pricing
- Offers and promotions
- Delivery fees and ETA
- Ratings and popularity signals
Such data fuels restaurant analytics, market research, and competitive benchmarking.
3. Restaurant & Cloud Kitchen Data
Direct restaurant data sources include:
- Menu structures
- Cuisine classification
- Portion sizes
- Price tiers
- Operating hours
This data is widely used for menu engineering and location-based demand analysis.
4. FMCG & Packaged Food Data
Food datasets also include packaged food intelligence such as:
- Brand and SKU-level data
- Ingredient lists
- Nutritional values
- Pack sizes and pricing
- Private-label vs branded products
These datasets support CPG analytics and product positioning strategies.
Types of Food Datasets

1. Product & Menu Datasets
These datasets capture:
- Food item names
- Categories and cuisines
- Ingredients and allergens
- Images and descriptions
They are fundamental for catalog intelligence and AI-based food recognition models.
2. Pricing & Promotion Datasets
Pricing datasets include:
- Base prices
- Discounted prices
- Coupons and offers
- Time-bound promotions
This data enables dynamic pricing models and promotional strategy optimization.
3. Availability & Inventory Datasets
Availability datasets track:
- In-stock vs out-of-stock status
- Store or location-level availability
- Item removals and substitutions
They are crucial for supply chain optimization and demand planning.
4. Delivery & Fulfillment Datasets
Delivery-related food datasets include:
- Estimated delivery time
- Delivery fees
- Surge pricing indicators
- Pickup vs delivery options
These datasets help evaluate logistics performance and customer experience.
5. Ratings & Popularity Datasets
Consumer-facing datasets capture:
- Ratings and reviews
- Bestseller tags
- Popular cuisines
- Trending food items
They are used for demand forecasting and trend analysis.
6. Nutrition & Ingredient Datasets
Nutrition-focused food datasets include:
- Calories and macronutrients
- Ingredients and allergens
- Dietary classifications (vegan, gluten-free, etc.)
These datasets support healthtech, nutrition apps, and regulatory analysis.
How Food Datasets Are Collected
Web Scraping as a Primary Data Source
Web scraping plays a central role in building food datasets. It enables automated extraction of publicly available data from food-related digital platforms at scale.
Key advantages of scraping-based food datasets:
- Real-time data collection
- Large-scale coverage across platforms
- Hyperlocal and location-specific insights
- Cost-effective data acquisition
Scraping is especially critical where official APIs are unavailable or limited.
API-Based Data Collection
In some cases, food datasets are delivered via:
- Data APIs
- Partner integrations
- Enterprise data feeds
APIs provide structured and stable access but often lack the breadth and flexibility of scraping-based datasets.
Key Use Cases of Food Datasets

1. Pricing Intelligence & Competitive Analysis
Retailers and brands use food datasets to:
- Monitor competitor pricing
- Track discount cycles
- Analyze price elasticity
- Optimize pricing strategies
This is essential in highly competitive food markets.
2. Menu Engineering & Product Optimization
Restaurants and cloud kitchens analyze food datasets to:
- Identify best-performing items
- Optimize menu pricing
- Reduce low-performing SKUs
- Launch data-backed food concepts
3. Demand Forecasting & Trend Analysis
Historical food datasets help businesses:
- Predict demand spikes
- Identify seasonal trends
- Track cuisine popularity
- Optimize inventory planning
4. Supply Chain & Inventory Optimization
Food datasets support:
- Stockout prediction
- Replenishment planning
- Waste reduction
- Vendor performance analysis
This leads to more resilient food supply chains.
5. AI & Machine Learning Applications
Food datasets are foundational for:
- Recommendation engines
- Price optimization models
- Food image recognition
- Nutrition scoring algorithms
AI-powered food intelligence depends on high-quality, structured datasets.
6. Market Research & Investment Analysis
Consultants and investors use food datasets to:
- Evaluate market size
- Analyze platform growth
- Track consumer behavior
- Assess competitive positioning
Challenges in Building Food Datasets

Despite their value, food datasets present challenges:
- Highly dynamic pricing and availability
- Frequent platform UI changes
- Data inconsistency across regions
- Language and currency variations
- Data normalization complexity
Professional data engineering and scraping frameworks are required to maintain accuracy.
Ethical & Responsible Use of Food Datasets
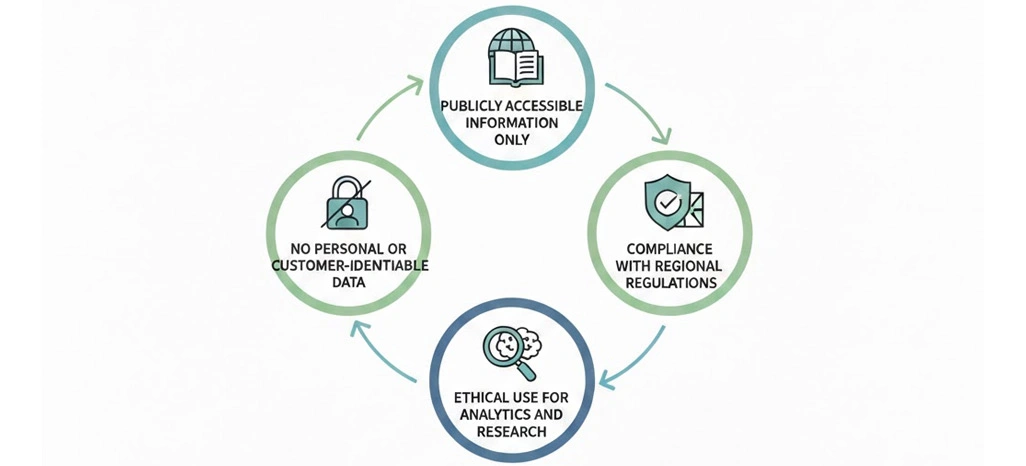
Responsible food data collection focuses on:
- Publicly accessible information only
- No personal or customer-identifiable data
- Compliance with regional regulations
- Ethical use for analytics and research
This ensures long-term sustainability and trust.
Future of Food Datasets
The future of food datasets will include:
- Real-time streaming food data
- AI-driven demand prediction
- Hyperlocal consumption analytics
- Integrated grocery + food delivery datasets
- Smarter personalization models
As digital food platforms expand globally, food datasets will become a core strategic asset.
Conclusion
Food datasets are redefining how businesses understand pricing, demand, supply chains, and consumer preferences across the global food ecosystem. From grocery platforms and food delivery apps to restaurants, FMCG brands, and AI-driven startups, structured food data enables smarter, faster, and more informed decision-making.
As the food industry continues its digital transformation, organizations that invest in scalable, accurate, and real-time food datasets will gain a decisive competitive advantage. Turning raw food data into actionable intelligence is no longer optional—it is essential for growth and resilience.
For enterprises, analysts, and data-driven teams looking to build high-quality, structured, and scalable food datasets through ethical web scraping and APIs, Retail Scrape provides advanced food data extraction solutions designed to support research, analytics, and business intelligence at scale.
